My IP ↗or
My IP ↗orIn IPinfo's IP to Privacy Detection data, we have a category of anonymous IP service called "relay."
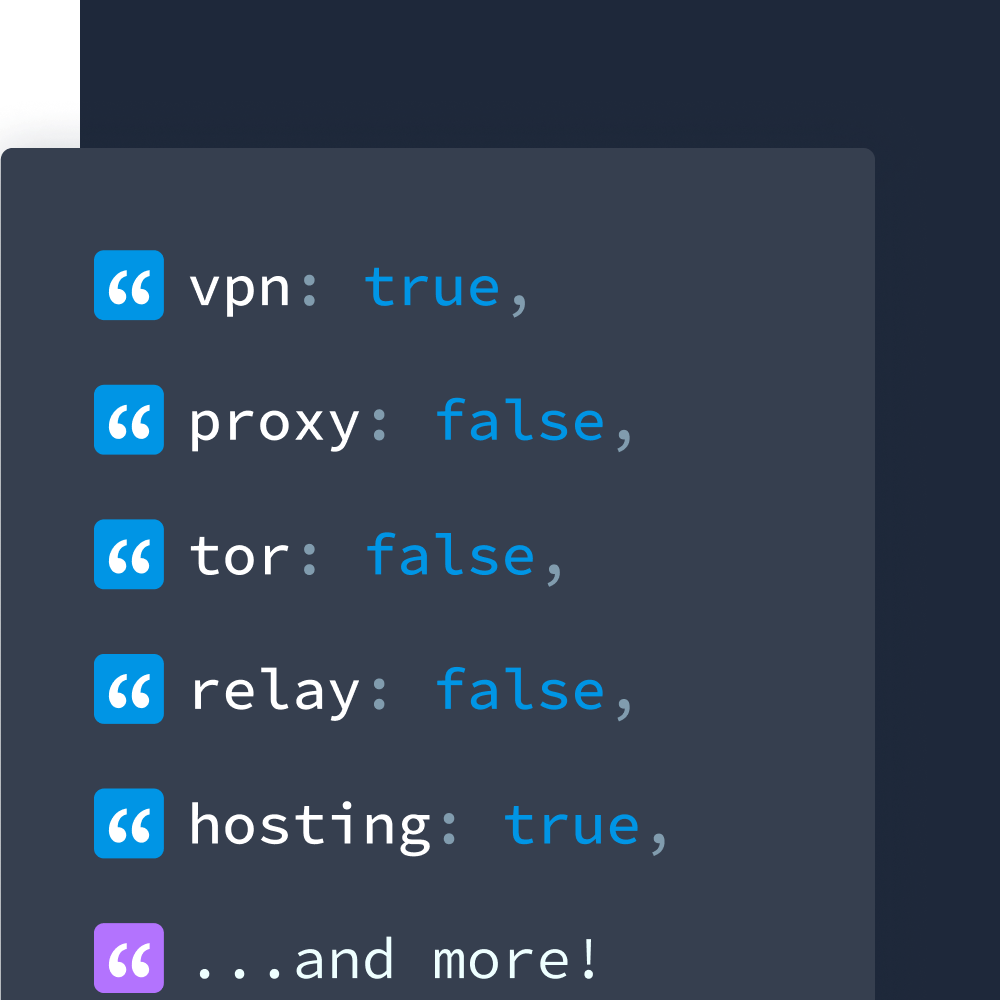
{
"vpn": false,
"proxy": false,
"tor": false,
"relay": true, <------------------
"hosting": true,
"service": "Apple Private Relay"
}
A relay service is an anonymous traffic forwarding service that still preserves a user’s general location. These include iCloud Private Relay, Google One Proxy, etc.
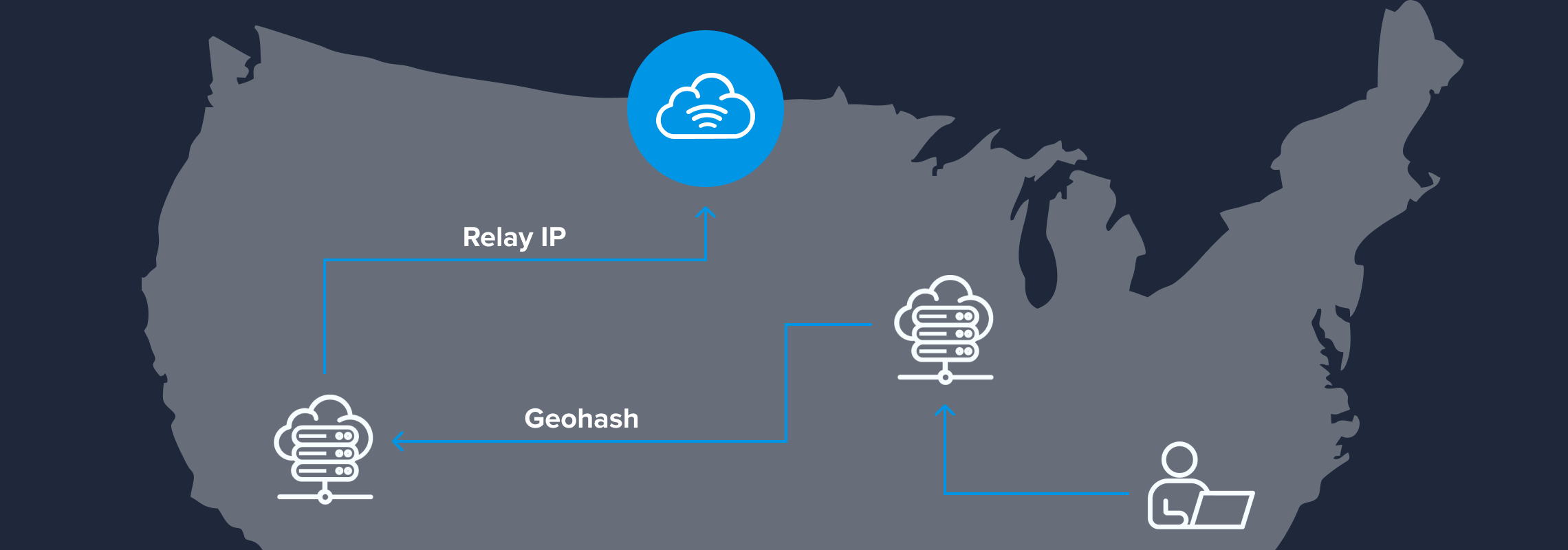
It is a privacy-focused IP anonymization technology that routes a user's internet traffic through two layers of intermediary servers to obscure their IP address while closely replicating the user's IP location. This means that internet traffic from and to the user is sent to relay servers before reaching the final destination, preventing the destination site from directly identifying the user's IP address.
How Is a Relay Different From a VPN?
A VPN routes all your traffic through a single server, hiding your IP address but not necessarily splitting the knowledge of your identity and browsing activity.
On the other hand, a private relay uses a two-server model: one server knows your IP address but not your browsing activity, and the other server (operated by a third party) knows your browsing activity but not your IP address, offering a higher level of privacy.
The Two-Server Model of Relays
In the iCloud Private Relay structure, DNS level encryption is done by Apple, then the traffic is sent to the secondary layer in which stage third party platforms tunnel the data through their own servers. These platforms include Cloudflare, Akamai, and Fastly.
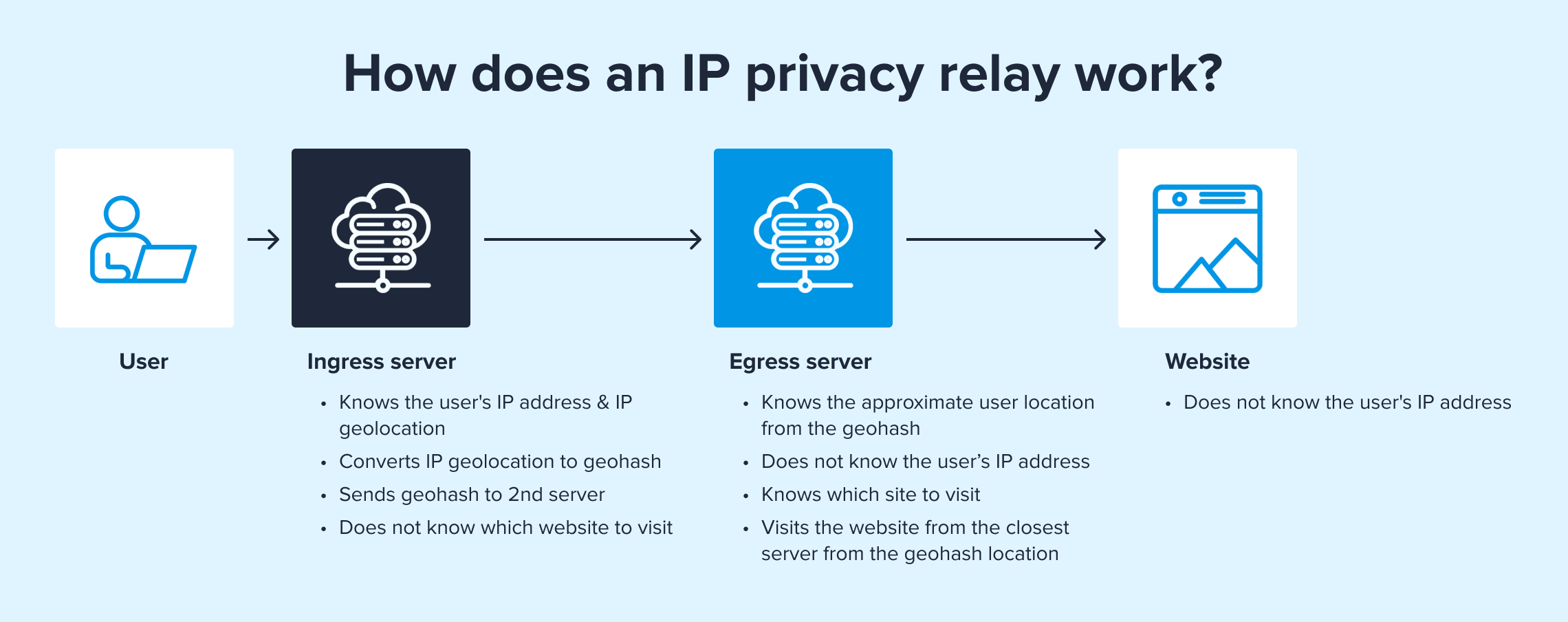
A private relay process thus involves two distinct servers:
- First Server: Operated by the relay service provider (e.g., Apple for their iCloud Private Relay). This server knows the visitor's IP address but not the destination website.
- Second Server: Operated by a third party or another entity, this server knows the destination website but not the visitor's IP address.
The first server strips or masks the visitor’s IP address before forwarding the request to the second server. The second server then processes the request and delivers it to the destination website, which only sees the IP address of the second server.
Anonymizing the IP Address While Preserving Geolocation
To preserve location information while anonymizing the IP address, the relay service can use geolocation databases that map IP addresses to approximate geographic locations. The relay servers may use these databases to provide location data based on the visitor's IP address without disclosing the IP address to the second server. This information is communicated to the second server with a geohash instead of sending the user's IP address.
A geohash is a short code that represents a specific geographic location. For example, the geohash u4pruy covers part of New York City, while u4pruydqqvj pinpoints a spot within a few meters. The longer the geohash, the more precise the location—shorter ones represent larger areas like cities or neighborhoods. In iCloud Private Relay, a four-character geohash is used, which covers roughly 800 square kilometers.
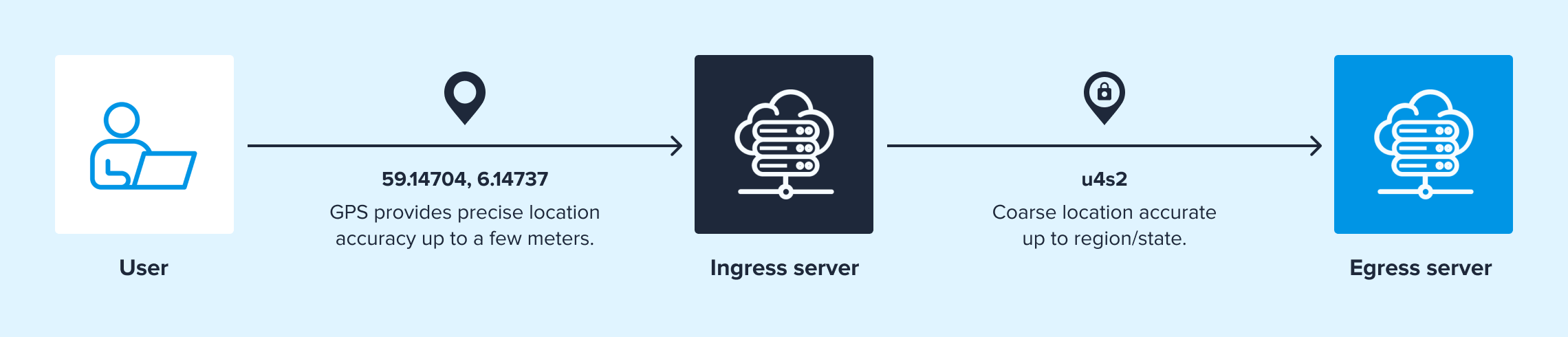
The second server platforms maintain a pool of IP addresses for the relay service. These IP addresses have been registered with geolocation database providers to correspond to specific cities worldwide.
When a relay user connects and presents the previously determined geohash, the closest matching IP address is selected. Servers see the IP address of the second server that corresponds to the original user IP address's location without obtaining information that may be used to identify the specific user.
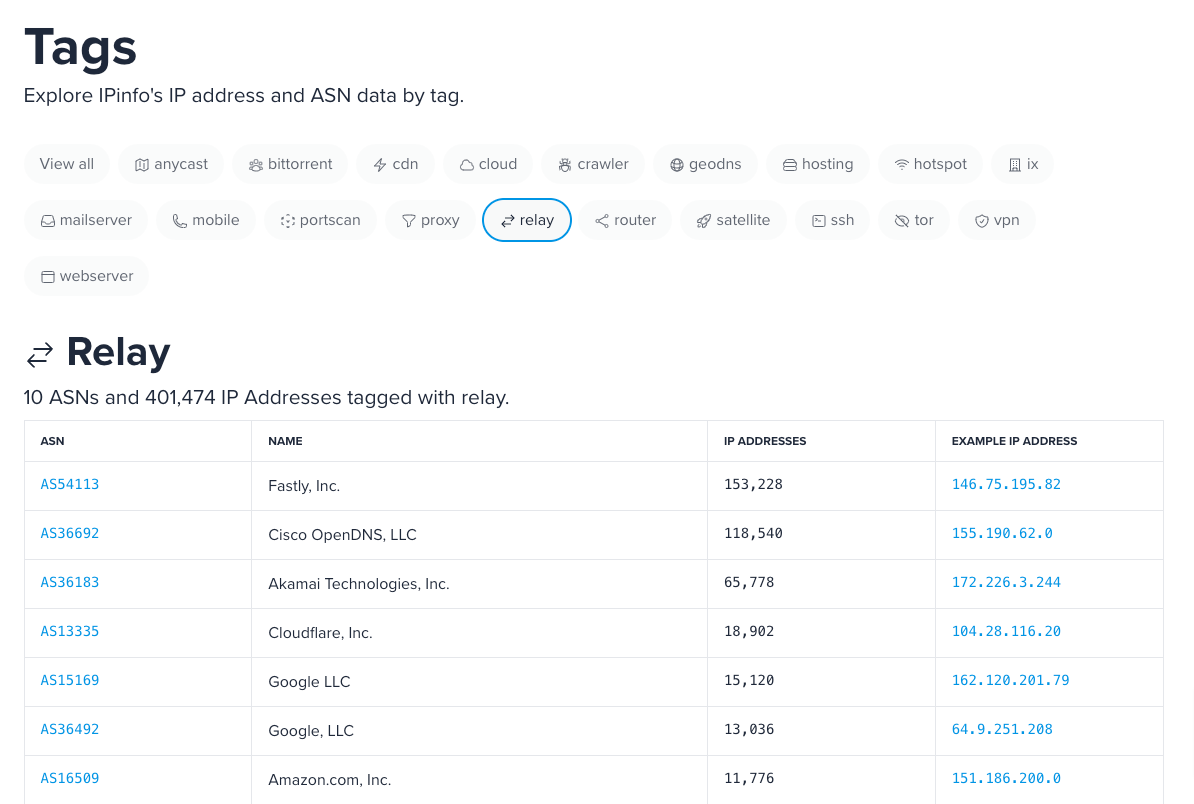
You can explore the relay IPs from our IP metadata tags page.
Detect Relay Services with IPinfo
Relay services anonymize IP addresses by routing your internet traffic through intermediary servers to obscure your IP address and protect your personal information. IP anonymizing technologies like these are becoming increasingly popular, and while they can be used with good intent, some users rely on these services to mask fraudulent activities or launch cyberattacks.
At IPinfo, we can detect relay IP addresses–along with VPNs, tors, and proxies–with our IP to privacy detection data, empowering our customers to get accurate insights into their usage.
Detect privacy services with ease
Tools that anonymize IP addresses can be exploited by bad actors to launch cyber attacks. Stop them in their tracks.
About the author

Abdullah leads the IPinfo internet data community and he also works on expanding IPinfo’s probe network of servers across the globe.